Nutrition is The Foundation of Health

Nutrition is a cornerstone of health and well-being, influencing everything from physical fitness to mental clarity. It encompasses the intake of food and nutrients necessary for the body to function properly, grow, and repair itself. As the foundation of a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition is crucial in preventing diseases, promoting overall health, and enhancing the quality of life. Understanding the importance of nutrition can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that lead to better health outcomes.
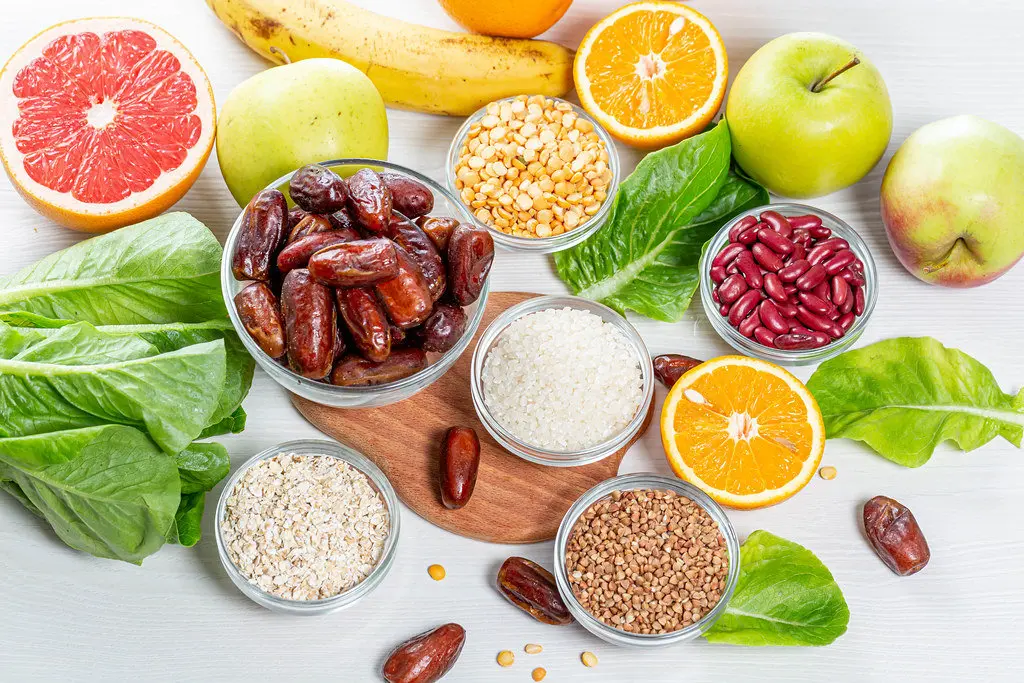
At the most fundamental level, nutrition provides the essential nutrients that the body needs to perform its myriad functions. These nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Each plays a unique role in maintaining health. Carbohydrates serve as the body’s primary energy source, while proteins are vital for building and repairing tissues. Fats, although often misunderstood, are crucial for hormone production, nutrient absorption, and brain health. Vitamins and minerals are necessary for various biochemical processes and overall bodily functions, from immune response to bone health.
A well-balanced diet rich in whole foods—fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats—provides the body with a spectrum of nutrients required for optimal functioning. Consuming a variety of foods ensures that individuals receive the necessary vitamins and minerals to support their immune system, maintain energy levels, and promote healthy growth and development. For instance, vitamin C found in citrus fruits is essential for immune function, while calcium and vitamin D play critical roles in maintaining bone health.
Proper nutrition is also crucial for the prevention of chronic diseases. Unhealthy dietary patterns, characterized by excessive consumption of processed foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, contribute significantly to the rise of non-communicable diseases such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. Studies have consistently shown that a diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, coupled with regular physical activity, can significantly reduce the risk of these chronic conditions.
The relationship between poor nutrition and the rise of obesity and diabetes is particularly alarming. When individuals consume a diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugars, it leads to excessive calorie intake and poor satiety signals, increasing the likelihood of weight gain. Obesity, defined as having an excess amount of body fat, is a significant risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. In fact, nearly 90% of individuals with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese.
The excess body fat, especially visceral fat surrounding the abdomen, leads to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This results in elevated blood sugar levels and can ultimately lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. Moreover, high-fat diets—particularly those high in saturated and trans fats—can lead to inflammation, which further exacerbates insulin resistance and increases the risk of metabolic syndrome.
In addition to physical health consequences, poor nutrition also impacts mental well-being. Emerging research suggests that there is a strong link between diet and mental health. Nutrient deficiencies can contribute to mood disorders, anxiety, and cognitive decline. For example, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish are associated with improved mood and cognitive function, while a diet rich in antioxidants can help protect against oxidative stress linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Eating a balanced diet can support mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall cognitive health, making it a crucial aspect of holistic well-being.
For children and adolescents, proper nutrition is especially critical. The formative years are a time of rapid growth and development, making it essential to provide young individuals with the nutrients they need to thrive. A healthy diet supports cognitive development, enhances academic performance, and fosters lifelong healthy eating habits. Teaching children about nutrition and involving them in meal planning and preparation can help instill a sense of ownership over their dietary choices, promoting healthier habits that last into adulthood.
The importance of nutrition extends beyond individual health to encompass community well-being. Food security, access to nutritious foods, and health education are critical components of public health. Communities that prioritize nutrition can foster healthier populations, reduce healthcare costs, and improve quality of life. Initiatives that promote access to healthy foods, such as farmers’ markets and community gardens, as well as educational programs that teach cooking and nutrition skills, can empower individuals to make healthier choices and create a culture of wellness.
In conclusion, nutrition is a vital element in ensuring proper health and well-being. It supports physical and mental health, prevents chronic diseases, aids in weight management, and plays a crucial role in child development. Poor nutrition, characterized by excessive intake of processed foods and insufficient consumption of fruits and vegetables, significantly increases the risk of obesity, diabetes, and related chronic diseases. By prioritizing balanced nutrition and making informed dietary choices, individuals can take proactive steps toward enhancing their health and improving their quality of life. The importance of nutrition extends beyond personal choices to encompass broader community health, making it imperative for society to promote access to healthy foods and nutrition education. Investing in nutrition is an investment in a healthier, more vibrant future for individuals and communities alike.